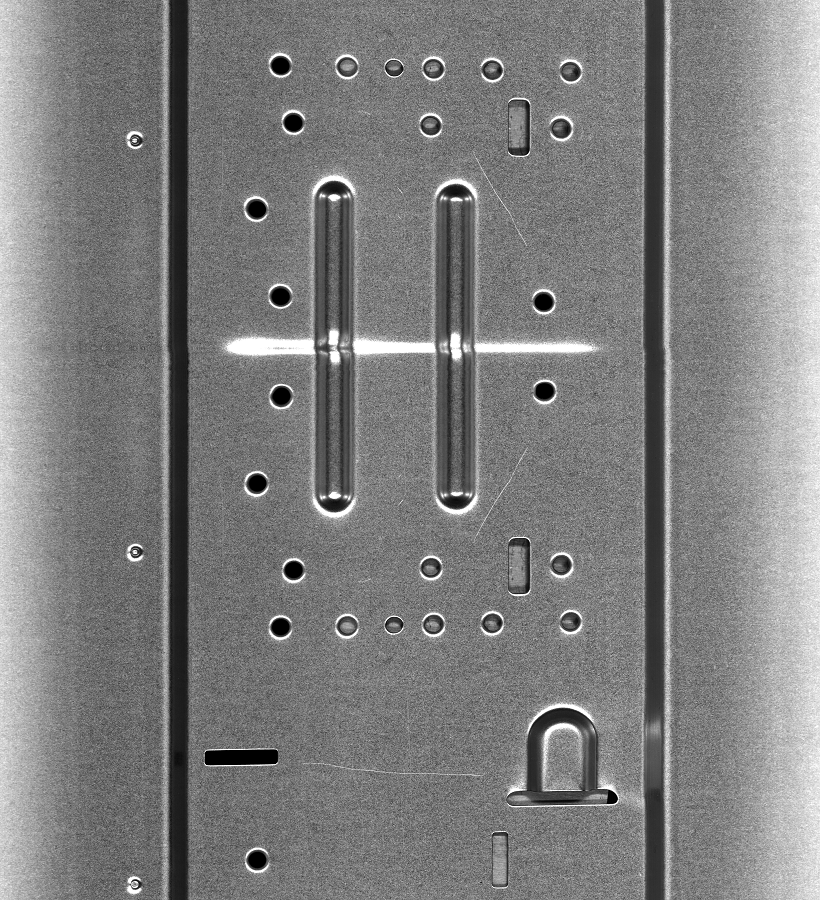
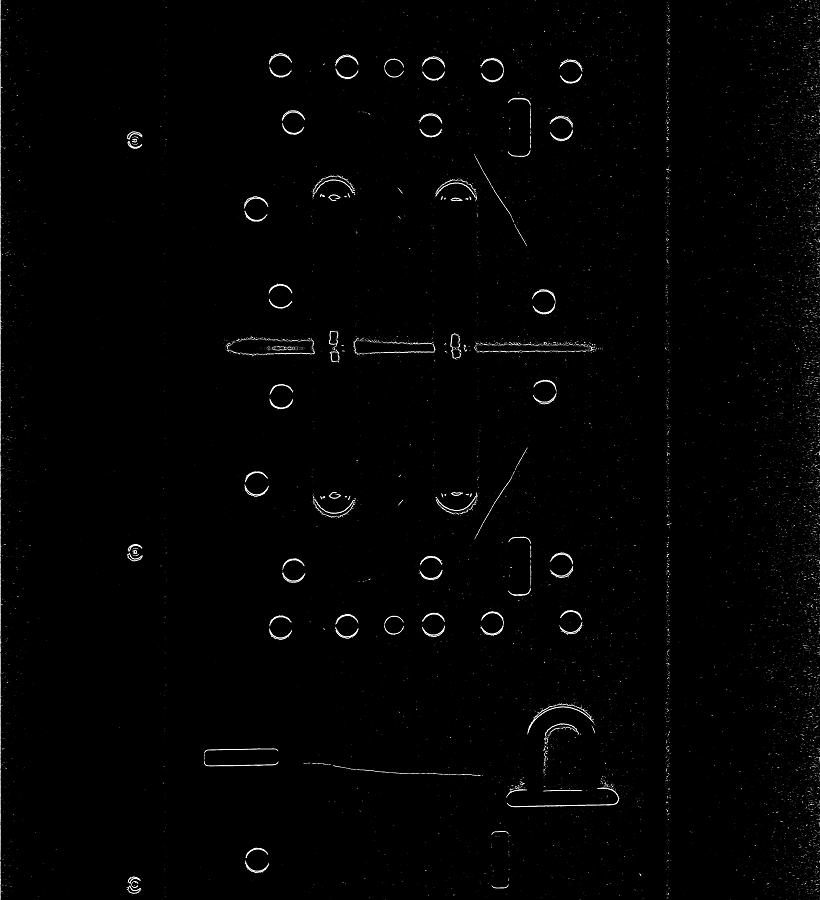
子像素的边缘检测算法很多,但使用CUDA进行的不是很多。github上可以找到一个带CUDA的子像素边缘检测算法,但经过运行发现有些小bug,其cpu版本正常,但gpu版本找轮廓时会偶发轮廓被切断的问题。一下就对其进行一些修正。当然也许还有其他bug~~
一.源项目位置
源项目位置https://github.com/CsCsongor/subPixelEdgeDetect 。算法基于论文https://www.ipol.im/pub/art/2017/216/
二.代码分析
通过分析,主要是因为使用CUDA后,导入了线程。而原有CPU算法是单线程的。在涉及到最优前向轮廓或最优后向轮廓的求解时,会因为多线程,导致没有找到最优轮廓,而保留了2个轮廓信息。
就是源算法中cu_chain_edge_points这个函数里的下面这段代码
if (fwd >= 0 && next[from] != fwd && ((alt = prev[fwd]) < 0 || chain(alt, fwd, Ex, Ey, Gx, Gy, rows, cols) < fwd_s)){
if (next[from] >= 0){ // Remove previous from-x link if one */
prev[next[from]] = -1; // Only prev requires explicit reset */
}
next[from] = fwd; // Set next of from-fwd link */
if (alt >= 0){ // Remove alt-fwd link if one
next[alt] = -1; // Only next requires explicit reset
}
prev[fwd] = from; // Set prev of from-fwd link
}
if (bck >= 0 && prev[from] != bck && ((alt = next[bck]) < 0 || chain(alt, bck, Ex, Ey, Gx, Gy, rows, cols) > bck_s)){
if (alt >= 0){ // Remove bck-alt link if one
prev[alt] = -1; // Only prev requires explicit reset
}
next[bck] = from; // Set next of bck-from link
if (prev[from] >= 0){ // Remove previous x-from link if one
next[prev[from]] = -1; // Only next requires explicit reset
}
prev[from] = bck; // Set prev of bck-from link
}
而原作者好像也发现了这个问题,在拼接所有轮廓的时候,并没有使用cpu版本里的代码去先找每一个轮廓的起始点,然后再拼接轮廓,而是从任意点开始。这样就会导致轮廓被切断了。
以下list_chained_edge_points 函数中的注释掉的那行代码,就是找轮廓起始点的算法。
// Set k to the beginning of the chain, or to i if closed curve
// for (k = i; (n = prev[k]) >= 0 && n != i; k = n); //这句被注释了,替换成了下面这行
if ((n = prev[i]) >=0 && n != i){ k= n;}
三.算法修改
1.修改cu_chain_edge_points函数。 寻找最优5*5轮廓点的算法屏蔽,先记录下所有向前向后轮廓点
// Chain edge points
__global__
void cu_chain_edge_points(int * next, int * prev, double * Ex, double * Ey,double * Gx, double * Gy, int rows, int cols){
int x, y, i , j, alt;
int dx, dy, to;
x = blockIdx.x*blockDim.x+threadIdx.x+2;
y = blockIdx.y*blockDim.y+threadIdx.y+2;
// Try each point to make local chains
// 2 pixel margin to include the tested neighbors
if (x < (rows-2) && y < (cols-2)){
// Must be an edge point
if (Ex[x + y*rows] >= 0.0 && Ey[x + y*rows] >= 0.0){
int from = x + y*rows; // Edge point to be chained
double fwd_s = 0.0; // Score of best forward chaining
double bck_s = 0.0; // Score of best backward chaining
int fwd = -1; // Edge point of best forward chaining
int bck = -1; // Edge point of best backward chaining
/* try all neighbors two pixels apart or less.
looking for candidates for chaining two pixels apart, in most such cases,
is enough to obtain good chains of edge points that accurately describes the edge.
*/
for (i = -2; i <= 2; i++){
for (j = -2; j <= 2; j++){
to = x + i + (y + j)*rows; // Candidate edge point to be chained
double s = chain(from, to, Ex, Ey, Gx, Gy, rows, cols); //score from-to
if (s > fwd_s){ // A better forward chaining found
fwd_s = s;
fwd = to;
} else if (s < bck_s){ // A better backward chaining found
bck_s = s;
bck = to;
}
}
}
if (fwd >= 0){
next[from] = fwd; // Set next of from-fwd link
}
if (bck >= 0){
prev[from] = bck; // Set prev of bck-from link
}
// if (fwd >= 0 && next[from] != fwd && ((alt = prev[fwd]) < 0 || chain(alt, fwd, Ex, Ey, Gx, Gy, rows, cols) < fwd_s)){
// if (next[from] >= 0){ // Remove previous from-x link if one */
// prev[next[from]] = -1; // Only prev requires explicit reset */
// }
// next[from] = fwd; // Set next of from-fwd link */
// if (alt >= 0){ // Remove alt-fwd link if one
// next[alt] = -1; // Only next requires explicit reset
// }
// prev[fwd] = from; // Set prev of from-fwd link
// }
// if (bck >= 0 && prev[from] != bck && ((alt = next[bck]) < 0 || chain(alt, bck, Ex, Ey, Gx, Gy, rows, cols) > bck_s)){
// if (alt >= 0){ // Remove bck-alt link if one
// prev[alt] = -1; // Only prev requires explicit reset
// }
// next[bck] = from; // Set next of bck-from link
// if (prev[from] >= 0){ // Remove previous x-from link if one
// next[prev[from]] = -1; // Only next requires explicit reset
// }
// prev[from] = bck; // Set prev of bck-from link
// }
}
}
}
2.增加一个cu_cut_edge_points函数来完成单点最后向前向后轮廓的选择,切掉不是最优的轮廓
__global__
void cu_cut_edge_points(int * next, int * prev, double * Ex, double * Ey,double * Gx, double * Gy, int rows, int cols){
int x, y, i , j, alt;
int dx, dy, to;
x = blockIdx.x*blockDim.x+threadIdx.x+2;
y = blockIdx.y*blockDim.y+threadIdx.y+2;
if (x < (rows-2) && y < (cols-2)){
if (Ex[x + y*rows] >= 0.0 && Ey[x + y*rows] >= 0.0){
int center = x + y*rows;
int temp_next = -1;
int temp_prev = -1;
if (x < (rows-2) && y < (cols-2)){
for (i = -2; i <= 2; i++){
for (j = -2; j <= 2; j++){
to = x + i + (y + j)*rows;
if(next[to] == center){
if(temp_next >= 0){
if(chain(center, to, Ex, Ey, Gx, Gy, rows, cols) > chain(center, temp_next, Ex, Ey, Gx, Gy, rows, cols)){
next[temp_next] = -1;
temp_next = to;
} else {
next[to] = -1;
}
} else {
temp_next = to;
}
}
if(prev[to] == center){
if(temp_prev >= 0){
if(chain(center, to, Ex, Ey, Gx, Gy, rows, cols) < chain(center, temp_prev, Ex, Ey, Gx, Gy, rows, cols)){
prev[temp_prev] = -1;
temp_prev = to;
} else {
prev[to] = -1;
}
} else {
temp_prev = to;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
3.修改cu_thresholds_remove函数,删掉一些错误的轮廓
__global__
void cu_thresholds_remove(int * next, int * prev,int rows, int cols, int * valid){
int x, y;
x = blockIdx.x*blockDim.x+threadIdx.x;
y = blockIdx.y*blockDim.y+threadIdx.y;
int idx = x+y*rows;
if (idx < rows*cols){
if ((prev[idx] >= 0 || next[idx] >= 0) && !valid[idx]){
prev[idx] = next[idx] = -1;
}
if(prev[idx] != -1 && next[prev[idx]] != idx){
prev[idx] = -1;
}
if(next[idx] != -1 && prev[next[idx]] != idx){
next[idx] = -1;
}
}
}
4.修改list_chained_edge_points函数,重新启用找寻轮廓起始点的代码
// Set k to the beginning of the chain, or to i if closed curve
for (k = i; (n = prev[k]) >= 0 && n != i; k = n);
//if ((n = prev[i]) >=0 && n != i){ k= n;}
5.修改devernay函数,增加刚才添加的函数
cu_chain_edge_points<<<numberOfBlocks, threadsPerBlock, threadsPerBlock.x*threadsPerBlock.y*sizeof(uchar), stream>>>(next, prev, Ex, Ey, Gx, Gy, rows, cols);
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
cu_cut_edge_points<<<numberOfBlocks, threadsPerBlock, threadsPerBlock.x*threadsPerBlock.y*sizeof(uchar), stream>>>(next, prev, Ex, Ey, Gx, Gy, rows, cols);
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
cu_thresholds_with_hysteresis<<<numberOfBlocks, threadsPerBlock, threadsPerBlock.x*threadsPerBlock.y*sizeof(uchar), stream>>>(next, prev, modG, rows, cols, th_high, th_low, valid);
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
完整的代码请下载 subPixelGPU.zip